Numerous celestial phenomena surround the vast expanse of the universe, captivating astronomers and space enthusiasts. Due to its unique characteristics and significance, Stars-923 has recently drawn attention among those who study stellar formations and cosmic phenomena.
In this article, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive guide about this fascinating object. This guide will serve not only the experts in the field but also space enthusiasts who are eager to expand their knowledge.
What is Stars-923?

Stars-923 refers to the classification or group of stars that exhibit unique characteristics and significance in studying stellar evolution and cosmic behavior. These groups of stars are often studied for their spectral emissions, luminosity, and magnetic fields.
The data recovered from this study is then used for broader astronomical research, including understanding stellar evolution and galaxy formation.
Physical Characteristics of Stars-923
1. G-type main-sequence star: Stars-923 is classified as a G-type main-sequence star due to its surface temperature, which ranges between 5,300 and 6,000 K.
2. Size: Its size is approximately 0.9 times that of the Sun. The size suggests that his star is a relatively modest star in terms of brightness and mass.
3. Age: Stars-923 is approximately 6 billion years old, placing it in the middle of its main sequence phase. According to its age, this star is expected to continue its hydrogen-burning phase for several billion more years before evolving into a red giant or a white dwarf.
4. Chemical Composition: Its chemical composition resembles that of the Sun. It includes elements such as hydrogen, helium, and various other metals.
Discovery of Stars-923
In 2023, this space object was first discovered by an international team of astronomers using the latest space telescope technology. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was used to discover these stars.
JWST developed powerful infrared imaging capabilities that allowed astronomers to penetrate the dense clouds of dust and gas.
It was discovered as part of a broader survey of celestial objects in the unexplored region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The discovery has significantly expanded the astronomers’ abilities to analyze distant celestial objects.
However, it also helped them to reveal the extraordinary properties of Stars-923 that set it apart from the countless other stars.
Understanding the Structure and Formation of Stars-923
The structure of this fascinating object is marked by different layers that include the core where nuclear fusion occurs, the radiative zone, and the convective zone. Each of these layers plays a crucial role in the lifecycle of stars.
Stars-923 is made of various elements mostly found in massive stars, including helium, hydrogen, and traces of heavier elements like oxygen and carbon. These elements result in the nuclear fusion that lights up the stars.
Below, we have discussed different stages of the formation of this celestial phenomenon.
1. Stellar Nurseries: It is the first and most crucial stage in the formation of Stars 923. These nurseries are rich in creating new stars. Gas and dirt come collectively to form clumps under the influence of gravity, forming protostars. Over the years, these protostars transform into full-fledged stars, ready to embark on a cosmic journey.
2. Nuclear Fusion: At this stage, the elements that stars are made of result in nuclear fusion. This process is very important to power every star, as it is at the coronary heart of every star. Hydrogen atoms combine to shape helium during the process, releasing massive energy. This vast energy is the reason that these stars shine so much.
3. Classification: After stars form, they are classified into different types based on size and temperature. These classifications include giants and dwarf stars with different traits and life tiers. This classification helps astronomers gain insights into the evolution and behavior of stars.
4. Main Sequence Phase: During this phase, Stars-923 becomes solid and stable due to the balance between the gravitational force pulling inward and the radiation pushing outwards. Depending on the size and temperature of the stars, this phase can last for millions to billions of years.
Classification and Types of Stars-923
Stars-923 are classified into different types, from large giants to tiny dwarfs, based on their size and temperature. These classifications provide insights into their life cycles and interactions within the galactic properties.
Below, we will discuss each classification system with a complete
1. Spectral Classes
Stars are classified into spectral classes based on their temperature and the absorption lines in their spectra. Massive and very hot stars with temperatures over 30,000 K come under the O spectral class.
These stars emit a blue light and have strong ionized helium lines. Here are some other classes;
A. Stars between 10,000 and 30,000 K temperatures are classified as B class. They are blue-white and have strong helium lines.
B. A class has white or bluish stars with temperatures between 7,500 and 10,000 K.
C. Yellow-white stars with temperatures between 6,000 and 7,500 K come under the F class. They have strong metallic and hydrogen lines.
D. Giant stars like the Sun with temperatures 5,200 and 6,000 K are in G class.
E. Orange stars with temperatures between 3,700 and 5,200 K and strong lines of neutral metals and molecules belong to the K class.
F. Cool, red stars with temperatures below 3,700 K are classified as M Class. These stars have strong molecular bands and neutral metal lines.
2. Luminosity Classes
Stars are also classified into luminosity classes, which describe their brightness relative to their size. These are;
A. Supergiants: These are among the largest and most luminous stars, significantly more massive than the Sun. They exceed 10 to 70 times the Sun’s mass. There are two main types of supergiants, red and blue supergiants.
B. Bright Giants: Bright giants are large, luminous, and somewhat less bright than supergiants. These stars are often visible even from great distances, with a radius ranging about 10 to 100 times that of the Sun.
C. Subgiants: These stars are a transitional type of star in a phase between the main sequence and the giant stage of stellar evolution. With hydrogen fuel in their cores, they expand and cool.
D. Main Sequence Stars: These are the superstars of a premium collection. Hydrogen burning at their core gives them solidity. Depending on their mass, these stars can last tens of millions to billions of years.
3. Additional Categories
In addition to spectral and luminosity classes, some stars fall into additional categories;
1. White Dwarfs: When a star like the Sun has gone through its main sequence and red giant phases, it sheds its outer layers, leaving behind a dense and hot core, which is no longer undergoing nuclear fusion. This core is called a white dwarf.
2. Red Dwarfs: Red dwarfs are small, cool stars characterized by their low mass, ranging from 0.08 to 0.6 times that of the Sun. Their relatively low temperatures give them a reddish appearance.
3. Neutron Stars: When a star with a mass about 1.4 to 2.1 times that of the Sun exhausts its nuclear fuel, it undergoes a catastrophic collapse. The core contracts under gravity and protons and electrons merge to form neutrons, which form neutron stars.
What is the Role of Stars-923 in the Galaxy?
This fascinating space object plays a significant role in the galaxy’s shape and dynamics. It contributes to the formation of planetary systems, influences the development of stellar nurseries, and distributes heavy elements through supernova explosions.
It helps shape the galaxy’s structure and contributes to the ongoing life cycles of stars forming and dying. During the supernova explosion and nuclear fusion, these stars produce elements, such as carbon, oxygen, and iron, which are vital building blocks of planets.
These elements enrich the interstellar medium and provide unheated materials of destiny luminaries and planetary bodies.
Importance of Stars-923 Study in Astrophysical Research
It is a normal space study with significant implications for understanding the broader universe. The study of Stars-923 provides;
1. Stellar Evolution
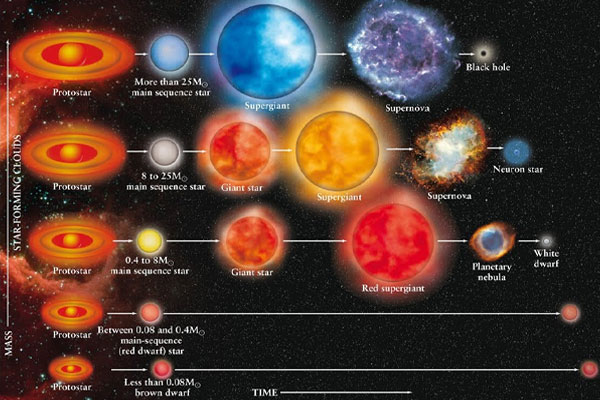
One of the primary areas related to this study is stellar evolution. It reveals the red supergiant in this classification is approaching the end of its life. However, the supernova mechanism will provide valuable data on the final stages of massive star evolution.
The study allows astronomers to observe the pre-supernova conditions of Stars-923. As a result, it helps them to refine their models of how supernovae occur and what factors influence the outcomes.
2. Galactic Dynamics
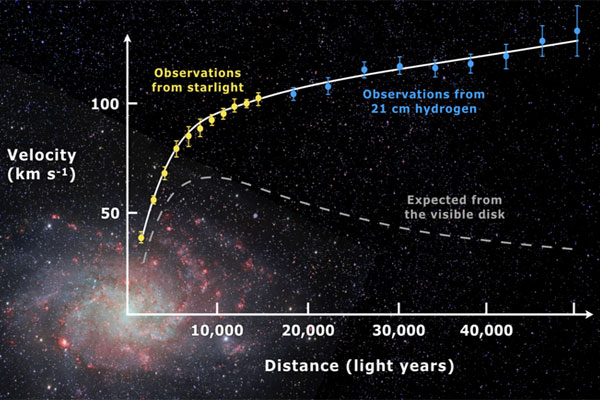
The study also contributes to understanding the galaxy’s dynamics and structure. Its position in the Milky Way provides clues about the distribution and movement of stars. However, researchers can also gain insights into the galaxy’s broader dynamics by analyzing the stars’ trajectory and interactions.
3. Gravitational Waves
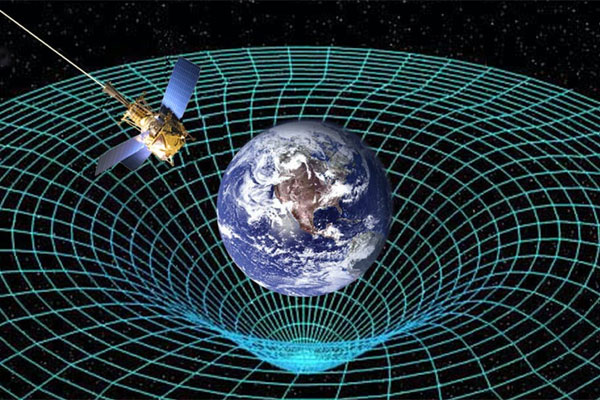
The dynamic interaction between the neutron star and red supergiant holds significant implications for a broader understanding of gravitational waves. Compact objects like neutron stars are prime sources of gravitational waves.
Studying these will help scientists better understand their sources and characteristics. It could also provide insights into the nature of gravity and the structure of spacetime.
4. Cosmic Chronology
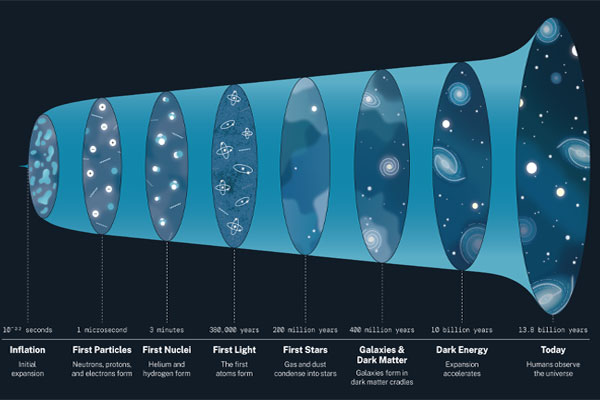
Star-923’s study also plays a crucial role in cosmic chronology. It helps scientists establish a timeline for the formation and evolution of the stellar population within the Milky Way. Astronomers can refine galactic history and evolution models by comparing the star’s physical characteristics with other stellar clusters.
5. Spectroscopy
It is a technique used to analyze the light emitted from Stars-923. This study will help scientists to determine its composition, temperature and various other vital properties. It involves splitting light into its colors, resulting in a spectrum.
The spectrum is then analyzed to realize the gift of chemical elements.
Cultural Significance of Stars-923
For the duration of records, these stars served as navigational aids, symbols of wish, and metaphors for human circumstances. Due to their clinical hobbies, they reflect their significance in human records and imagination.
1. Stars 923 plays a significant role in mythology. They have created testimonies and legends, mirroring the deep connection between humanity and the cosmos.
2. In earlier days, sailors and travelers depended on the stars to find their way. The positioning of stars helped them determine range and longitude.
3. Stars-923 has also inspired art and literature. They have inspired famous paintings like Vincent van Gogh’s “Starry Night,” poetry, thriller, and Marvel.
Challenges Faced While Studying Stars-923
Despite the advancements in observational technology, studying these stars presents challenges related to resolution, sensitivity, and data interpretation. The stars’ brightness and relative distance from Earth obstruct detailed observations.
Another challenge faced while studying these stars is searching exoplanets around Stars-923. While no confirmed planets have been detected, continued efforts to refine detection techniques and analyze signals hold promise for future discoveries.
What Future Does Studying Stars-923 Hold?
As technology advances, astronomers continue to explore new elements of stars in the universe. They are discovering exoplanets orbiting around Stars-923 and gravitational waves, which will provide insights into the cosmos.
It will broaden our understanding of stars. However, exploring exoplanets will also help scientists better understand planetary diversity and the potential for existence beyond Earth.
On the other hand, the discovery of gravitational waves helps astronomers analyze more about stars, including black hole mergers and neutron collisions. It also provides information about cosmic events.
It also contributes to the bigger structure of the universe called the cosmic web, a massive network of interconnected filaments composed of darkish galaxies. It also provides insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies.
Wrapping Up
Stars-923 represents a fascinating subject of study within the field of astronomy. They offer valuable insights into the nature of G-type stars and their role in the broader context of stellar and galactic evolution.
Through ongoing research and technological advancements, scientists continue to unravel the mysteries of this celestial object, contributing to an understanding of the universe.







